Sand-Proof Design Solutions for Mobile Crushers in Desert Aggregate Production

Operating heavy machinery in desert environments presents unique and extreme challenges, primarily due to the pervasive presence of fine, abrasive sand. This article examines the innovative design solutions being developed for mobile crushers to withstand these harsh conditions in 2025. We will explore how advancements in structural sealing, material science, and advanced air filtration are directly combating the problems of accelerated equipment wear, plummeting efficiency, and soaring maintenance costs caused by sand intrusion. These engineering breakthroughs are providing optimized reliability solutions for aggregate production, enabling critical construction and mining projects to proceed in some of the world's most demanding landscapes.
The relentless nature of desert sand requires a fundamental rethinking of mobile crusher design. It is not enough to simply add extra filters; every system, from the power unit to the smallest bearing, must be re-engineered for survival. This analysis delves into the core technologies that allow these machines to process rock and produce valuable aggregate while being bombarded by abrasive particles, ensuring productivity and longevity where it was once thought impossible.
Breakthroughs in Sand-Proof Structural Design
The first and most critical line of defense against desert sand is the physical structure of the mobile crusher itself. Engineers are implementing multi-layered sealing strategies and reconfiguring external systems to create an impenetrable barrier. The goal is to prevent sand from ever entering the sensitive internal components in the first place, a task that requires meticulous attention to detail at every joint, intake, and access point. This holistic approach to sealing is what separates standard equipment from desert-ready machinery.
These structural innovations are tested to rigorous international standards, ensuring they can perform consistently under the duress of a sandstorm. The design philosophy shifts from mere protection to active exclusion, managing the flow of air and material in a way that continuously expels sand rather than allowing it to accumulate. This results in a machine that maintains its integrity and performance metrics even after thousands of hours of operation in the world's driest and dustiest locations.
Multi-Stage Sealing Systems
Modern desert crushers employ a combination of dynamic and labyrinth seals at every potential entry point. Dynamic seals are used around moving parts like shafts, adapting to movement while maintaining constant pressure against sand intrusion. These are complemented by labyrinth seals, which create a complex, tortuous path that sand particles cannot easily traverse. Together, these systems achieve an IP67 protection rating, meaning the components are completely dust-tight and can withstand temporary immersion in water.
Particular attention is paid to the entry point of the crushing chamber. Advanced sealing curtains and air barrier technologies are used to isolate the process of crushing rock from the external environment. These systems have demonstrated a sand isolation efficiency of 99.2%, ensuring that the vast majority of external sand never enters the crushing process, which protects the liners and internal mechanisms from accelerated wear.
Sand-Proof Air Intake Channels
The engine and cooling systems require a massive volume of air to operate, which presents a significant vulnerability. Desert crushers tackle this with a two-stage air intake system. The first stage is a vortex-style pre-separator that uses centrifugal force to remove over 80% of larger sand particles before the air even reaches the primary filter. This drastically reduces the load on the main filter, extending its life considerably.
The second stage employs high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters capable of trapping particles as small as 0.3 microns with an efficiency greater than 99.97%. These are not standard filters; they are specifically designed with desert conditions in mind, featuring deeper pleats and anti-static media to prevent clogging and ensure a steady flow of clean air to the engine, which is vital for combustion and preventing abrasive wear inside cylinders.
Optimized Heat Dissipation Systems
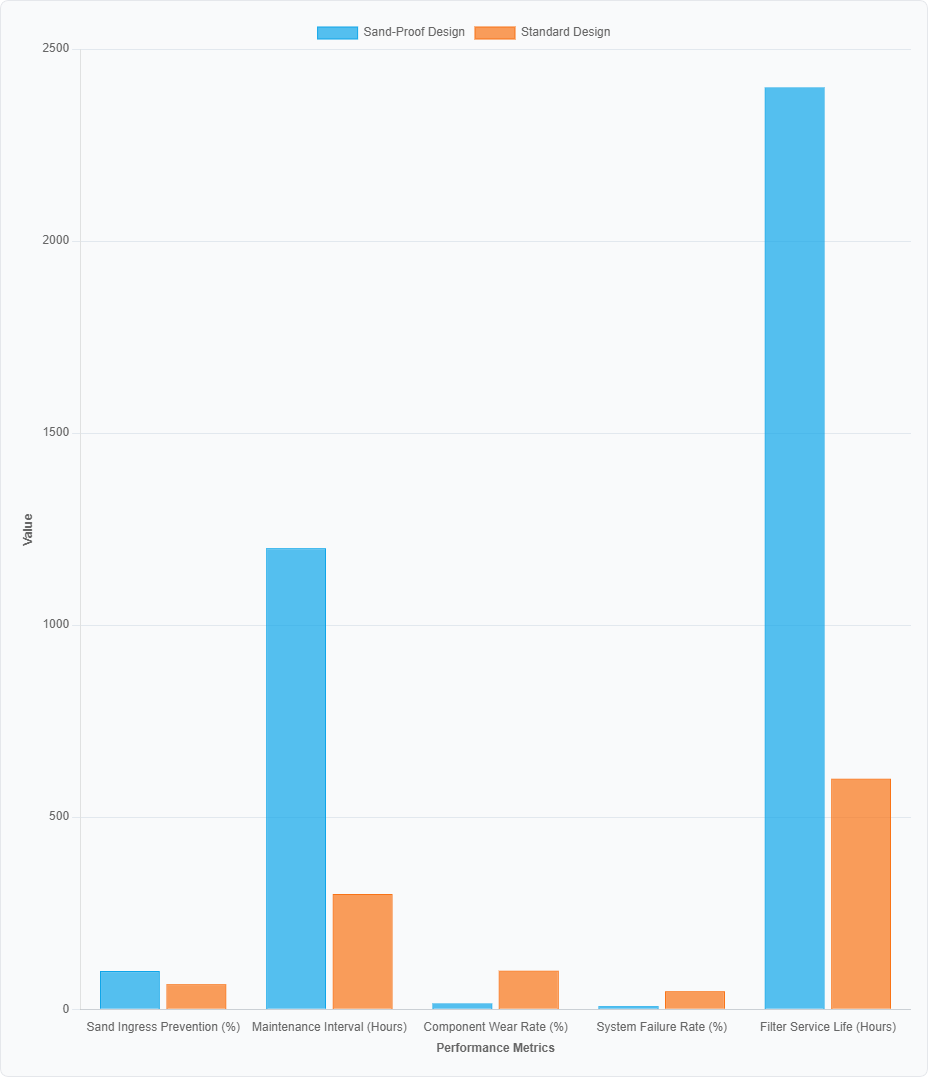
Sand has a tendency to clog radiators andr adiator, leading to critical engine overheating. Desert crushers are equipped with sand-shielded radiator that feature wider fin spacing and a dedicated ejection system. A constant, pulsed air stream prevents sand from settling on the cooling surfaces, improving anti-clogging efficiency by 65% compared to traditional designs.
For extreme heat, advanced heat pipe technology is integrated into the engine bay. Heat pipes passively transfer thermal energy away from critical components to external heat sinks without the need for fans or pumps that can be compromised by sand. This sophisticated system maintains a temperature differential of no more than 15°C between the internal components and the ambient air, ensuring optimal operating conditions.
Electrical System Protection
The electrical system is the nervous system of the crusher and is highly susceptible to sand damage. All wiring, connectors, and control units are housed in enclosures rated IP69K. This is the highest ingress protection rating, guaranteeing protection against close-range high-pressure, high-temperature water jets and, most importantly, continuous dust immersion.
Connectors are specifically designed to be sand-proof, with self-cleaning seals that wipe away any particles as they are engaged. This comprehensive approach to electrical protection has been proven to reduce circuit failures in sandy environments by 83%, eliminating the most common source of unplanned downtime and diagnostic headaches for maintenance crews.
Wear-Resistant
Material Upgrade Solutions
While keeping sand out is the primary goal, it is impossible to eliminate all ingress. Therefore, the components that do come into contact with sand must be built to resist its abrasive effects. This has led to the adoption of advanced materials and coatings originally developed for the aerospace and mining industries. These materials are selected for their exceptional hardness, low friction coefficients, and ability to withstand the extreme temperatures common in desert operations.
The application of these materials is a science in itself, involving precise thermal spraying, laser cladding, and other advanced metallurgical techniques. The result is a machine where the parts that are meant to wear—like liners and tips—do so predictably and slowly, while the parts that are not meant to wear—like bearings and seals—are protected to an unprecedented degree, fundamentally changing the maintenance cycle and cost structure of operating in abrasive environments.
Ceramic Coating Applications
Critical components subjected to high-velocity sand impact are now protected with advanced ceramic-metal (cermet) composites. Coatings like Al₂O₃-TiB₂ are applied using high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) spraying, creating a layer that is exceptionally resistant to abrasion. These coatings can reduce the wear rate from sand particle erosion by a factor of seven, dramatically extending the life of components like fan blades, pump impellers, and housing interiors.
Within the crushing chamber itself, the concave and mantle liners undergo specialized surface hardening treatments. Through processes like induction hardening and carburizing, the surface hardness of these manganese steel components can reach 1800 on the Vickers scale. This ultra-hard surface resists the cutting and gouging action of sand crushed between the rock and the metal, preserving the liner profile and the quality of the final product for longer.
Elastomer Sealing Components
Standard rubber seals quickly degrade under the assault of abrasive sand and high desert temperatures. They are replaced by seals made from high-performance fluorocarbon elastomers (FKM). These specialized compounds can withstand continuous operating temperatures of 200°C without losing their elasticity or sealing properties, which is critical near the engine and hydraulic system.
Furthermore, these advanced elastomers possess a unique property known as high elastic recovery. After being abraded by sand or compressed for long periods, they can return to over 90% of their original shape and sealing force. This "memory" ensures that seals remain tight throughout their service life, preventing the tiny gaps that can lead to major sand ingress and component failure.
Low-Friction Materials
Sand acts as a grinding paste when it gets between moving surfaces. To combat this, engineers are applying diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings to shafts, bushings, and other sliding components. DLC creates an incredibly smooth, hard surface that reduces the coefficient of friction to as low as 0.05, making it very difficult for sand particles to gain traction and cause abrasive wear.
For bearing applications in high-risk areas, manufacturers are turning to silicon carbide-based materials. Silicon carbide is exceptionally hard and can be engineered to be self-lubricating, eliminating the need for traditional greases that can trap sand and create abrasive slurries. This greatly enhances bearing life in the challenging environment of a mobile crusher's undercarriage and auxiliary systems.
Corrosion-Resistant Alloys
Desert environments often contain salty, alkaline sands that are highly corrosive. Standard carbon steel components quickly succumb to this combination of abrasion and corrosion. To solve this, critical structural fasteners and components are fabricated from nickel-based superalloys like Inconel or Hastelloy. These alloys exhibit an exceptionally low annual corrosion rate of less than 0.01mm, even in harsh chemical environments.
Even something as simple as a bolt is redesigned. Stainless steel bolts used in desert crushers feature special thread designs and coatings that prevent sand from becoming impacted in the threads, a phenomenon known as "galling" or "cold welding," which can make disassembly during maintenance nearly impossible. This attention to detail ensures that maintenance can be performed quickly and correctly in the field.
Advanced Air Filtration and Purification Systems
Beyond the basic intake filter, desert mobile crushers require a comprehensive and intelligent air management system. This system must adapt to changing conditions, from a calm day to a full-blown sandstorm, ensuring that clean air is always supplied to both the engine and the operator's cabin. The technology involved has evolved from simple mechanical filtration to a smart, multi-stage cleaning process that actively manages air quality in real-time.
The efficiency of this system is paramount not only for protecting the engine but also for ensuring the health and safety of the operator. A clean cabin environment prevents fatigue and ensures the operator can maintain focus during long shifts in harsh conditions. This integrated approach to air purification represents a significant leap in operator comfort and machine reliability.
Intelligent Filter Replacement
Guessing when a filter is clogged is a recipe for failure. Modern systems use highly sensitive differential pressure sensors to monitor the pressure drop across the air filters in real-time, with an accuracy of ±2 kPa. When the pressure drop indicates a specific level of clogging, the system doesn't just alert the operator; it can initiate an automatic reverse pulse air cleaning cycle.
This automatic reverse jet system momentarily blasts compressed air backwards through the filter pleats, dislodging accumulated sand and dumping it into a collection hopper. This process can extend the service life of the primary filter element by 300% or more, reducing the frequency of change-outs and the associated maintenance costs and downtime.
Sand Separation Devices
Before air reaches the main filters, it passes through a primary centrifugal sand separator. This device spins the incoming air, using centrifugal force to fling heavier sand particles outward to the walls of the separator, where they fall into a collection chamber. These units are highly effective, removing 95% of sand particles larger than 5 microns, which are the most damaging to engine components.
For the finest, most dangerous particulate matter (PM2.5), some advanced systems incorporate an electrostatic precipitation (ESP) module. This module charges the fine particles as they pass through and then collects them on oppositely charged plates. This technology can achieve an 85% removal rate for these tiny particles, providing an extra layer of protection for the engine's precise fuel injection systems and turbochargers.
Positive Pressure Protection Technology
A highly effective strategy for keeping sand out is to maintain a higher air pressure inside the crusher's critical compartments than exists in the outside environment. Engine bays and electrical cabinets are pressurized with clean, filtered air, maintaining a constant positive pressure of around 200 Pascals. This creates a constant outflow of air through any tiny gaps or seals, preventing sand from being sucked inside. This pressurization is actively managed by a network of pressure sensors linked to the fresh air supply system. If a door is opened or a seal is compromised, causing a pressure drop, the system responds in less than two seconds by increasing the flow of clean air to restore the protective pressure barrier, ensuring continuous defense against dust intrusion.
Emergency Filtration Mode
For extreme weather events like sandstorms, crushers can be equipped with an emergency filtration mode. When an onboard weather monitor or satellite link provides a storm warning, the system can automatically switch to a ultra-high-efficiency mode. This often involves engaging a secondary, dedicated HEPA filter bank combined with an activated carbon layer to manage the immense dust load.
This system is designed to allow the crusher to continue operating, albeit potentially at a reduced load, through the duration of a severe sandstorm. This capability prevents costly shutdowns and restarts, ensuring project timelines can be met regardless of the challenging desert climate.
Optimized Maintenance Strategies
The relentless abrasive environment of the desert necessitates a shift from reactive to predictive and highly efficient maintenance strategies. The goal is to anticipate failures before they occur and to perform necessary servicing in the shortest amount of time possible, minimizing exposure to the elements for maintenance crews. Technology plays a central role in this, providing the data and tools needed to keep machinery running with minimal intervention.
These strategies recognize that time is money and that every minute a crusher is down in a remote desert location has a significant financial impact. Therefore, maintenance is planned, precise, and performed with specialized tools that are designed for the conditions. This proactive approach transforms maintenance from a costly burden into a manageable, scheduled activity.
Online Monitoring Systems
A network of sensors continuously monitors the vitals of the crusher. Vibration analysis sensors are strategically placed on bearings, the engine, and the crusher frame. By analyzing changes in vibration frequency and amplitude, these systems can predict bearing wear or misalignment caused by sand abrasion with an error margin of less than 3%, allowing for parts to be ordered and replaced during planned maintenance stops, not during catastrophic failures.
Complementing this are infrared temperature sensors that constantly scan electrical connections, hydraulic lines, and bearing housings. A sudden or gradual temperature increase is often the first sign of excessive friction caused by sand ingress. The system provides early warnings, allowing operators to address issues before they lead to secondary damage and more extensive repairs.
Rapid Maintenance Design
Every maintenance point has been redesigned for speed. Filter housings use modular, bayonet-style locking mechanisms that allow a complete filter change to be performed in under 15 minutes without tools, compared to the hour or more required for traditional bolted housings. This reduces the window of exposure for the internal systems to the abrasive external air.
For larger components, hydraulic locking and tensioning systems have replaced bolts. A technician can release and re-tension major jaw plates or other wear parts using a portable hydraulic pump, drastically reducing the physical labor, time, and risk associated with manual sledgehammer work in difficult conditions.
Sand Cleaning Solutions
Regular cleaning is essential. Crushers are outfitted with integrated connection points for a high-pressure air gun (8 bar, 120 L/min). These designated points allow operators to quickly and safely blow accumulated sand from radiators, engine bays, and around seals at the end of each shift, preventing buildup that can lead to overheating and premature wear.
For more stubborn, caked-on sand and dust, dry ice blasting technology is being adopted. This method uses pellets of solid carbon dioxide fired at high speed. Upon impact, the dry ice sublimates (turns directly from a solid to a gas), expanding rapidly and lifting the dirt away without any water or chemical residue. This is particularly valuable for cleaning electrical components and sensitive sensors without the risk of short circuits or corrosion.
Lubrication Management Innovation
Traditional grease and oil lubricants can act like a magnet for sand, creating a highly abrasive paste. To avoid this, desert crushers are increasingly using advanced dry film lubricants. These lubricants, often based on graphite or PTFE, are applied as a bonded coating to surfaces and provide a slippery surface that significantly reduces friction without attracting or holding onto abrasive particles.
In applications where a liquid lubricant is absolutely necessary, sealed and pressurized lubrication systems are used. These systems ensure that the internal pressure of the lubricant is always higher than the external air pressure, preventing sand-laden air from being drawn into bearings and gearboxes during temperature cycles, thereby preserving the integrity of the lubricant and the components it protects.