Impact Crusher Daily Maintenance and Care Guide

This comprehensive guide provides essential information for the proper daily maintenance and care of impact crushers. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance, extends equipment lifespan, and prevents unexpected downtime. We will cover daily inspection procedures, lubrication system maintenance, and electrical system safety measures. Following these maintenance practices helps maintain crushing efficiency and operational safety while reducing long-term operating costs.
Daily Inspection and Cleaning Procedures
Daily inspection and cleaning form the foundation of impact crusher maintenance. These routine checks help identify potential issues before they develop into major problems. Operators should perform visual inspections before starting equipment each day, looking for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Regular cleaning prevents material buildup that can affect crusher performance and lead to premature wear of components.
Proper documentation of daily inspections creates valuable records for tracking equipment condition over time. Maintenance logs should include observations, measurements, and any adjustments made during the inspection process. This historical data helps predict maintenance needs and plan repairs during scheduled downtime rather than experiencing unexpected breakdowns during operation.
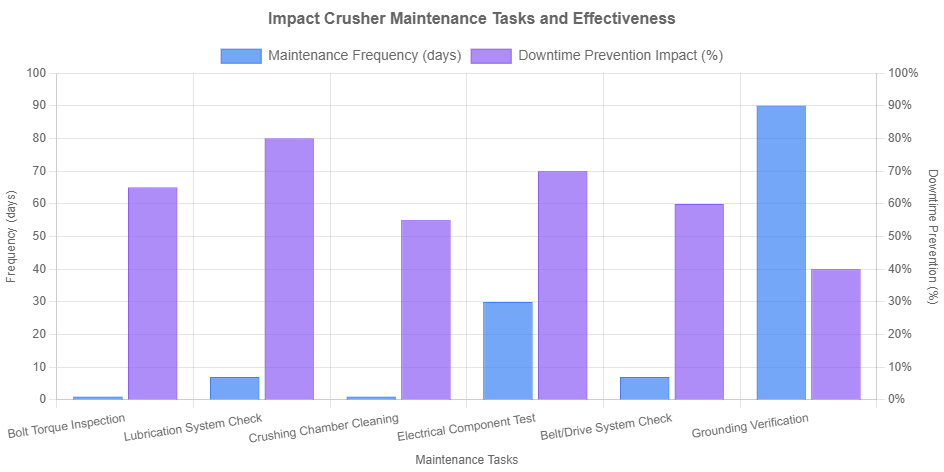
Exterior and Component Inspection Content
External inspections should include checking all bolt connections for proper tightness. Critical mounting bolts require verification with torque wrenches to ensure they meet manufacturer specifications, typically between 150-300 Nm depending on bolt size and location. Equipment sealing integrity must be verified, particularly around the crushing chamber and bearing housings where dust ingress can cause significant damage.
Drive system components require careful examination during daily inspections. V-belts should show no signs of cracking, glazing, or excessive wear. Proper belt tension is critical for efficient power transmission and typically allows about 10-15 mm deflection midway between pulleys. Chain drives require lubrication verification and inspection for stretched links or worn sprockets. All guards and safety devices must be secure and functional before equipment operation.
Cleaning Methods for Crushing Chamber and Discharge Area
The crushing chamber requires regular cleaning to remove material buildup that affects crushing efficiency. Operators should use specialized tools like long-handled brushes and scrapers designed for this purpose. Compressed air systems effectively remove dust from electrical components and hard-to-reach areas, though proper respiratory protection must be worn during this process. Never use sharp tools that might damage protective liners or other internal components.
Discharge areas and discharge size adjustment mechanisms need particular attention during cleaning. Accumulated material around adjustment cylinders or springs can prevent proper operation and affect product grading. Regular cleaning ensures material flows freely through the discharge area without blockages. After cleaning, operators should verify that all adjustment mechanisms move freely and maintain their settings during operation.
Lubrication System Maintenance and Care
The lubrication system is vital for impact crusher operation, reducing friction and heat generation in moving components. Proper lubrication extends bearing life and maintains crushing efficiency. Different crusher components require specific lubrication types and intervals based on their operating conditions and load requirements. A systematic approach to lubrication ensures all points receive adequate lubrication at appropriate intervals.
Lubrication records should be maintained to track service intervals and consumption rates. Unexpected changes in lubricant consumption often indicate developing problems such as seal failures or excessive wear. Modern crushers may feature automatic lubrication systems that require monitoring rather than manual application, though these systems still need regular inspection and maintenance.
Lubricant Selection Principles
Lubricant selection must follow manufacturer recommendations for viscosity and performance specifications. Most impact crushers require ISO VG 150-220 viscosity grade lubricants for bearings operating under normal conditions. Extreme temperatures or heavy loads may require synthetic lubricants with better thermal stability and oxidation resistance. Lubricants should contain appropriate additives for wear protection, rust prevention, and foam suppression.
Environmental conditions significantly influence lubricant selection. High-temperature environments require lubricants with higher viscosity indexes and better thermal stability. Wet or humid conditions demand lubricants with enhanced water separation properties and corrosion inhibitors. Operators should consult lubricant suppliers for recommendations specific to their operating conditions and crusher model.
Lubrication Point Lubrication and Inspection Methods
Manual lubrication points require proper technique using grease guns with the correct fitting type. Operators should purge old lubricant until fresh grease appears at seal edges, indicating complete filling of the cavity. Over-greasing can damage seals and cause overheating, while under-greasing leads to inadequate lubrication. Automatic lubrication systems need regular inspection to ensure proper operation and delivery to all points.
Lubrication point inspections should check for seal integrity and any signs of leakage. Contaminated lubricant appearing at grease points indicates seal failure requiring immediate attention. Bearing temperature checks after operation help identify lubrication problems, with temperatures typically remaining 20-30°C above ambient under normal conditions. Abnormal temperature rises suggest lubrication issues or mechanical problems needing investigation.
Electrical System Maintenance and Safety
Electrical system maintenance ensures safe and reliable crusher operation. Regular inspections prevent electrical failures that can cause unexpected downtime or safety hazards. Electrical maintenance should only be performed by qualified personnel following proper lockout-tagout procedures. Documentation of electrical inspections helps track component performance and plan preventive replacements.
Electrical system maintenance includes cleaning components to prevent dust buildup that can cause overheating or short circuits. Connections should be checked for tightness and signs of overheating. Insulation resistance testing helps identify deteriorating insulation before complete failure occurs. All electrical work must comply with local regulations and safety standards.
Electrical Component Inspection Content
Motor inspections include checking winding insulation resistance, which should exceed 1 megohm for most industrial motors. Bearings require lubrication according to manufacturer intervals, typically every 2,000-4,000 operating hours. Vibration analysis helps identify developing bearing problems before failure occurs. Controller inspections verify proper operation of protection devices and control functions.
Electrical measurements provide valuable information about system health. Voltage measurements should remain within ±10% of nominal rating, while current measurements should not exceed motor nameplate values. Phase imbalance should remain below 5% to prevent motor overheating. Power quality issues like harmonic distortion may require additional investigation and mitigation measures.
Equipment Grounding and Lightning Protection Methods
Proper equipment grounding is essential for electrical safety and noise reduction. Ground resistance should measure below 25 ohms for most applications, with lower values required in areas with high lightning risk. Grounding connections must be tight and free from corrosion, with regular verification of continuity. All electrical enclosures and non-current-carrying metal parts require bonding to the grounding system.
Lightning protection systems divert strike energy away from sensitive electrical equipment. Surge protection devices should be installed at electrical service entrances and major equipment connections. These devices require regular inspection for damage and replacement when indicated by status indicators. Grounding electrodes for lightning protection must have low impedance paths to earth to effectively dissipate energy from strikes.