Analysis of Key Points in Stone Crusher Maintenance: Maintenance Strategies to Ensure Reliable and Stable Operation

This article provides an in-depth examination of the essential maintenance practices required for stone crushers, which are vital machines in material processing industries. These
powerful machines apply immense mechanical force to reduce large rocks and ores into smaller, usable aggregates. Maintaining their operational integrity is paramount for
productivity and safety. We will explore systematic approaches to daily inspections, scheduled servicing, and effective troubleshooting. The guidance offered here is designed to
equip operators and maintenance teams with the knowledge to prolong equipment life and minimize costly downtime, ensuring these critical assets perform reliably under demanding
conditions.
The Critical Role of Daily Inspection Routines
Implementing a consistent daily inspection protocol forms the first line of defense against unexpected equipment failure. These checks are designed to identify minor issues before they escalate into major problems, safeguarding the crusher's operational continuity. A thorough visual examination of the machine's exterior and all connection points can reveal early signs of wear or loosening components.
Monitoring the lubrication system is another fundamental aspect of the daily routine. Checking oil levels and assessing the quality of the lubricant for contamination ensures that all moving parts are properly protected from excessive friction. Simultaneously, observing the electrical system for any irregularities in performance and measuring the temperature and vibration levels of transmission components provide valuable data on the machine's health.
Planning and Executing Periodic Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance is a proactive strategy that involves a series of planned tasks performed at specific intervals. This systematic approach is crucial for replacing components that experience predictable wear, such as those within the crushing chamber. Establishing a clear replacement cycle for these parts prevents sudden breakdowns and maintains product quality.
Maintenance intervals also include critical services for the hydraulic system, such as cleaning and replacing filters to ensure optimal pressure and flow. Adjusting and testing the spring tension and overload protection mechanisms guarantees the crusher can safely handle unforeseen hard or unbreakable materials. Furthermore, comprehensive cleaning and applying anti-corrosion treatments protect the equipment from environmental damage.
Understanding Common Failures and Their Origins
Equipment failures can generally be categorized into mechanical, electrical, and hydraulic issues. Mechanical problems often manifest as unusual noises, decreased output, or visible damage to crushing components like jaws or liners. These failures frequently stem from abrasive wear, improper feed material, or incorrect operational settings.
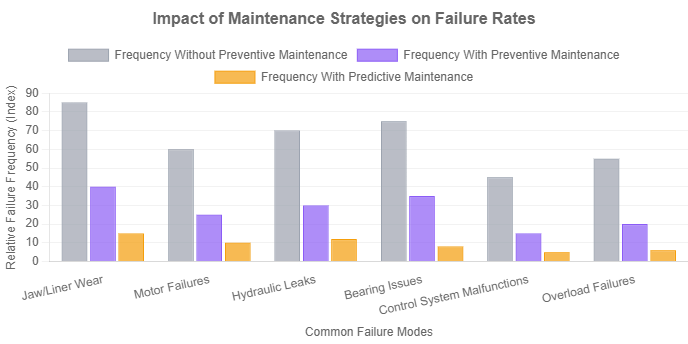
Electrical faults may include motor failures or disruptions in the control circuitry, which can halt operations entirely. Hydraulic system complications, such as leaks or pressure inconsistencies, often originate from seal degradation or pump inefficiencies. Analyzing the root cause of any malfunction requires a thorough understanding of the operating conditions and material characteristics.
Systematic Troubleshooting and Repair Procedures
Effective troubleshooting begins with meticulously documenting the observed symptoms and the conditions under which the fault occurred. This record-keeping provides a solid foundation for analysis. A methodical approach advocates for investigating the simplest potential causes first before progressing to more complex system checks.
Skilled use of diagnostic tools, from basic wrenches to advanced vibration analyzers, is essential for accurate problem identification. Once a repair is executed, rigorous testing under controlled conditions is necessary to verify the solution's effectiveness and ensure the crusher returns to its specified operational parameters.
Leveraging Maintenance Data for Improved Management
Maintaining detailed and standardized records of all maintenance activities transforms reactive repairs into predictable management. This historical data is invaluable for tracking component life cycles, understanding failure rates, and forecasting future maintenance needs. A well-structured log includes details of inspections, parts replacements, and operational hours.
Analyzing this data over time reveals trends and patterns that can predict potential failures, allowing for preemptive action. This data-driven strategy optimizes maintenance schedules, reduces spare parts inventory costs, and significantly enhances overall equipment efficiency. Implementing a digital database facilitates easy access and analysis of this critical information.
Developing a Skilled and Proactive Maintenance Team
The competence of the maintenance personnel is directly linked to the reliability of the stone crusher. Investing in continuous training ensures that team members are proficient in the latest diagnostic techniques and repair procedures. This training should cover the specific models of jaw crushers and cone crushers used on site.
Fostering an environment that values knowledge sharing from hands-on experience and case studies greatly enhances collective problem-solving skills. Establishing clear incentives boosts morale and encourages a sense of ownership and responsibility for the equipment's condition. Engaging with equipment manufacturers and industry peers provides access to valuable insights and emerging best practices, further elevating the team's capabilities and ensuring long-term operational success in various applications.